¶ DHCP Server
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server plays a central role in managing IP address assignments and network configuration in a computer network. Its primary functions are summarized in the Table below.
|
Feature |
Description |
|---|---|
| IP Address Assignment | The DHCP server allocates IP addresses dynamically to devices on the network as they connect. This ensures that devices have unique and valid IP addresses, reducing the likelihood of IP address conflicts. |
| Network Configuration | DHCP provides not only IP addresses but also essential network configuration parameters to connected devices, including subnet masks, default gateways, and DNS (Domain Name System) server addresses. This simplifies network configuration for users and administrators. |
| Lease Management | DHCP assigns IP addresses with lease durations, specifying how long a device can use the assigned address. When the lease expires, the device must renew the lease with the DHCP server. Lease management helps optimize IP address utilization and allows for efficient resource allocation. |
| Centralized Control | DHCP offers centralized control over IP address assignments and network parameters. This is critical for maintaining consistent network configurations, managing IP resources, and ensuring network security and compliance. |
| Scalability | DHCP is highly scalable, making it suitable for networks of all sizes, from small local networks to large enterprise environments. It adapts to the network's growth and dynamically manages IP address assignments. |
| IP Address Reservation | DHCP servers allow administrators to reserve specific IP addresses for particular devices, ensuring that critical resources receive consistent IP addressing. |
| Monitoring and Logging | DHCP servers often provide monitoring and logging capabilities that track IP address assignments and troubleshoot issues. This helps network administrators maintain visibility and control over the network. |
| Redundancy and Failover | When you deploy Exium's Cyber gateway in High Avaialbility (HA) mode, DHCP server is also replicated, ensuring that DHCP services remain available even in the event of a failure. |
As an integral part of Exium's Cyber Gateway (CGW), the DHCP server automates and streamlines the process of IP address assignment and network configuration, simplifying network management, optimizing resource allocation, and enhancing network efficiency.
¶ Configuring DHCP Server in Exium's platform
To configure DHCP server for a new Cyber Gateway deployment, follow the steps below.
- Navigate to the MSP admin console -> Client Workspace
- Click on Sites → CyberGateways in the left menu bar → Add Gateway if deploying a new CGW (Skip, if already deployed)
- If CGW already exists, then you can enable DHCP and configure range.
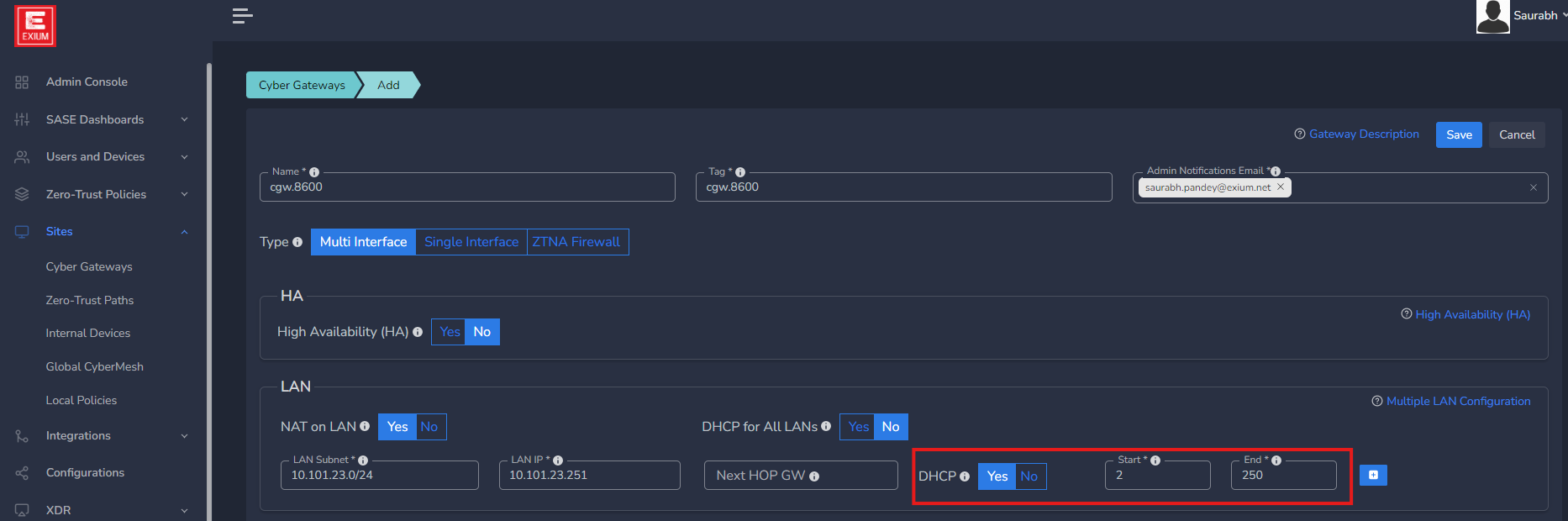
- Toggle the DHCP flag Yes (see screen shot below) for the LAN subnet
- Enter the subnet information in LAN Subnet. The DHCP server will allocate IP addresses from the subnet you enter here. In below screenshot is given as 10.101.23.0/24
- Start Range and End Range show IP range that needs to be allocated by DHCP server to end users and devices in the LAN network. Default starting IP is x.x.x.2 and Ending IP is x.x.x.250 (in this example Starting DHCP IP: 10.101.23.2 and End ip: 10.101.23.250).
- By default, if HA is not enabled for CGW, LAN Gateway IP .251 will be reserved. You may change it, but make sure same IP is not configured statically on any other devices in network to avoid IP conflict. If HA is enabled for CGW, LAN Gateway IP .1 will be reserved by default.
It is not recommended to use IPs above 250, because .251 and .252 IPs are reserved for CGW if it is deployed in HA mode for primary and secondary nodes respectively. You can edit start range and end range as per your requirement.
- In case of Multiple LAN interfaces, you can check below options, else skip it.
- If more than one LAN configured with their respective subnets, then you can enable or disable DHCP functionality individually for each LAN.
- You can specify ranges individually for each LAN subnet
- To enable or disable DHCP on all LAN interfaces, you can toggle button DHCP for All LANs to Yes or No.
- Click on “Save" or "Update”
- If this is for a new cyber gateway deployment, follow the instructions for Multiple interface CGW deployment